Supported Frameworks 🧱
Components from the following frameworks can be embedded in Vue and MDX files in :
- Vue (obviously)
- Preact
- SolidJS
- Svelte
- Vanilla JS
You must add a hydration directive when using non-Vue components in Vue and MDX files.
No JS is shipped if you use client:none 🏝
Choosing a Framework 🤔
While Vue is the natural choice given that pages and layouts in are Vue components, you might want to use a framework with a smaller runtime for the interactive bits.
For efficiency, you would want all islands to use the same framework, to offset the size of the runtime.
But before you leave and continue building your site…
Performance is Not Everything!
Several factors come into play when making this decision, such as development and maintenance costs.
For example, in the navbar of this site there are two islands:
<div class="flex items-center pl-6">
<DocSearch client:idle/>
<DarkModeSwitch client:load/>
</div>-
<DocSearch>is a Preact component.It's the heaviest component in this site, but I didn't have to build an accessible modal that works flawlessly in all devices and integrates with Algolia's search indexes.
-
<DarkModeSwitch/>is a Vue componentIt leverages useDark from
@vueuse/core, and uses a Vue<transition>when toggling the icon.It could be recreated using Svelte without additional dependencies, but the difference in bundle size for this site would be negligible, while risking the chance of introducing bugs.
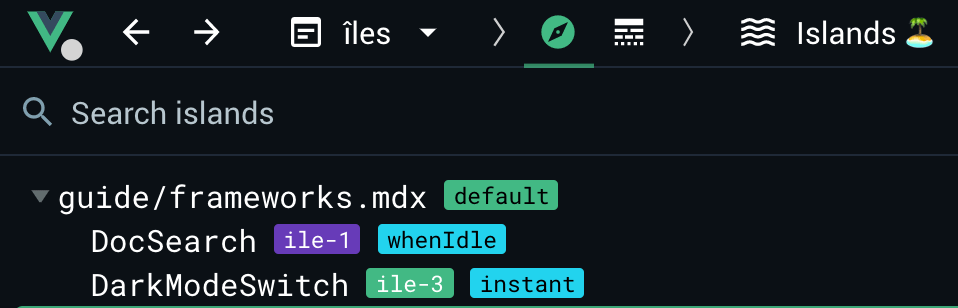
Preact and Vue islands from this page in DevTools
Which framework should you choose?It depends on the situation! There's no right answer or single metric to consider.
Bundle Size 📊
The following is a summary of the conclusions of a recent analysis that compares the final bundle size after adding the size of the framework runtime to the size of the compiled components:
If the amount of interactive components per page is
But that's just what one benchmark concluded!Do your own measurements, and as mentioned previously, there are often more important factors than bundle size. Choose according to your project's circumstances.